Spend any time at an online craft market like Etsy, and you'll notice a lot of the products there are 3D printed or include 3D-printed parts. But what do we actually mean by that, and how easy is it to start 3D printing your own items?
The answer isn't as simple as you might hope, but also not as complicated as you might fear.
How does a 3D printer work?
3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing that uses material to build layers into 3D objects. Essentially it prints by adding material (usually a form of plastic) one drop at a time. The 3D printer draws a shape on a flat surface and then draws another on top of it until the model is complete.
There are a lot of different types of materials used to create these layers, but the ones you're most likely to use as a hobbyist are melted plastic and UV resin. Which type you use will depend on the result you want to achieve. The best 3D printers automate a lot of the process, but there is still a lot of trial and error to get it right.
This picture shows one of the positives of owning a 3D printer. My colleague Dan Ackerman needed a mount for his iPhone to attach to his MacBook. A few hours and about $0.15 of material later, he had one up and running. It's satisfying to solve this kind of problem almost immediately.
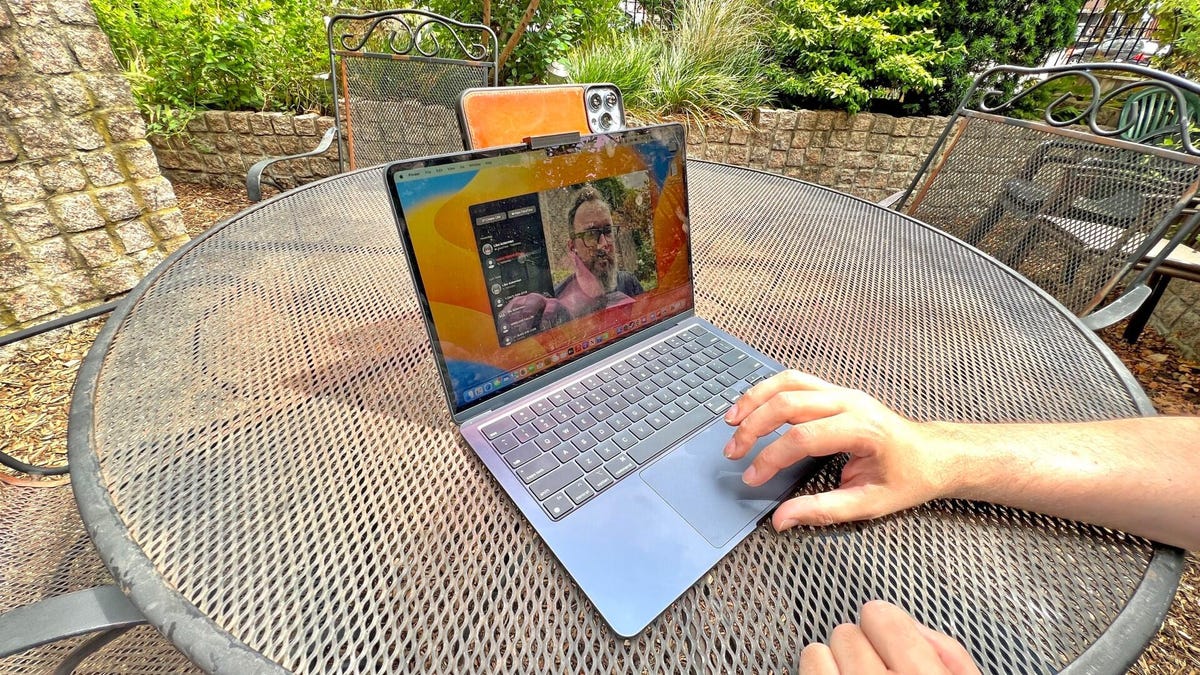

Making 3D printed parts save you time and money
Dan Ackerman/CNETWhat are the types of 3D printer?
Printers come in all different shapes and sizes and can be configured in various ways depending on your end goals, but most of the ones a hobbyist or small business will use can be broken down into two distinct types: FDM and resin.
Fused deposition modeling
This is the most common type of printer and the type most widely used by businesses and hobbyists. An FDM 3D printer is simply a plotting device. It pushes a plastic filament through a hot nozzle to squish layers into the print surface in a pattern.
There are a lot of different materials that you can use with an FDM printer. I won't go into detail here -- if you want more information, check out our list of the best 3D printer filaments -- but the simplest one to use is PLA. It's a type of non-toxic plant-based plastic that prints at fairly low temperatures.
You should buy an FDM 3D printer if you are looking to 3D print practical pieces, medium-sized decorative models and cosplay armor.
SLA (stereolithography) or resin 3D printing
SLA printing, more commonly known as resin printing, is almost the opposite of FDM printing. Instead of melting plastic into liquid, it uses a UV reactive liquid that's hardened under light. Each layer is "cured" using an LED array, which emits light in a set pattern.
Resin printing produces far more detailed models as an end result but it's a lot harder to work with. There are plenty of great resins out there for you to try but you need a wash-and-cure station to make sure they're safe to handle after you have printed them.
You should buy an SLA resin 3D printer if you want to print highly detailed models such as Dungeons and Dragons miniatures jewelry or even dentistry (assuming you're a dentist).
There is another process for 3D printing: Sintering uses a laser to fuse powder into shape. It's expensive and produces amazing results, but it requires large machines and plenty of space. It's certainly not great for use in your garage.

Even though it costs very little, this printer delivers excellent quality every time.
James Bricknell/CNETHow much is a 3D printer?
Prices for 3D printers vary wildly depending on what you want to do with them, how big the printer is and how detailed you want the models from the printer to be. We have a list of the best budget 3D printers on the site if you're looking for something under $500. Or we can recommend the best 3D printers overall if you have a little more money to spend. There are even semi-professional rigs that can cost a few thousand dollars.
The Neptune 2 is a good starting point for beginners. It's easy to set up and use and it's usually priced at under $200. While it isn't going to print the most detailed models, it will give you a good understanding of everything that 3D printing entails. The most important thing is that it's cheap, making it accessible.
If money's no object and you want an amazing in-home 3D printing experience, then the Prusa Mk3S Plus is the best choice. It comes in both kit and preassembled forms, but if you want to learn more about 3D printing you should buy the kit. It's an excellent introduction to how the whole process works, and it'll save you money.
At $799 plus shipping, it isn't the cheapest 3D printer, but it is the best out-of-the-box 3D printing experience money can buy. It's an investment when you're first starting out, but it can save you money in the long run: Some cheaper 3D printers require aftermarket upgrades and replacement parts to really shine.
In the four years that I've owned it, it's been my most consistent 3D printer in terms of reliability and output quality.
Resin 3D printers are similarly priced as their FDM counterparts, though the differences between the price point are more about speed and size than quality. A budget resin printer like the Anycubic M3 can be as low as $270 but the level of detail it can capture is as good as printers five times the cost. What keeps the price cheap is the size of the build area. Simply put; the more space you want the more you will expect to pay.
Is now a good time to buy a 3D printer?
3D printing is currently in a golden age. Unlike days past, when you needed an engineering degree to use a 3D printer, nowadays you can get set up and started with most printers in under 15 minutes.
Advanced safety features such as filament runout sensors and power loss protection are now standard even on budget-friendly options, so you're less likely to experience failures and more likely to succeed. That's not to say you'll never get failures -- you will, I promise. But failures are a good learning experience, and they won't be the majority of your results, like they used to be.
Source