Current Mortgage Rates: Compare Today's Rates
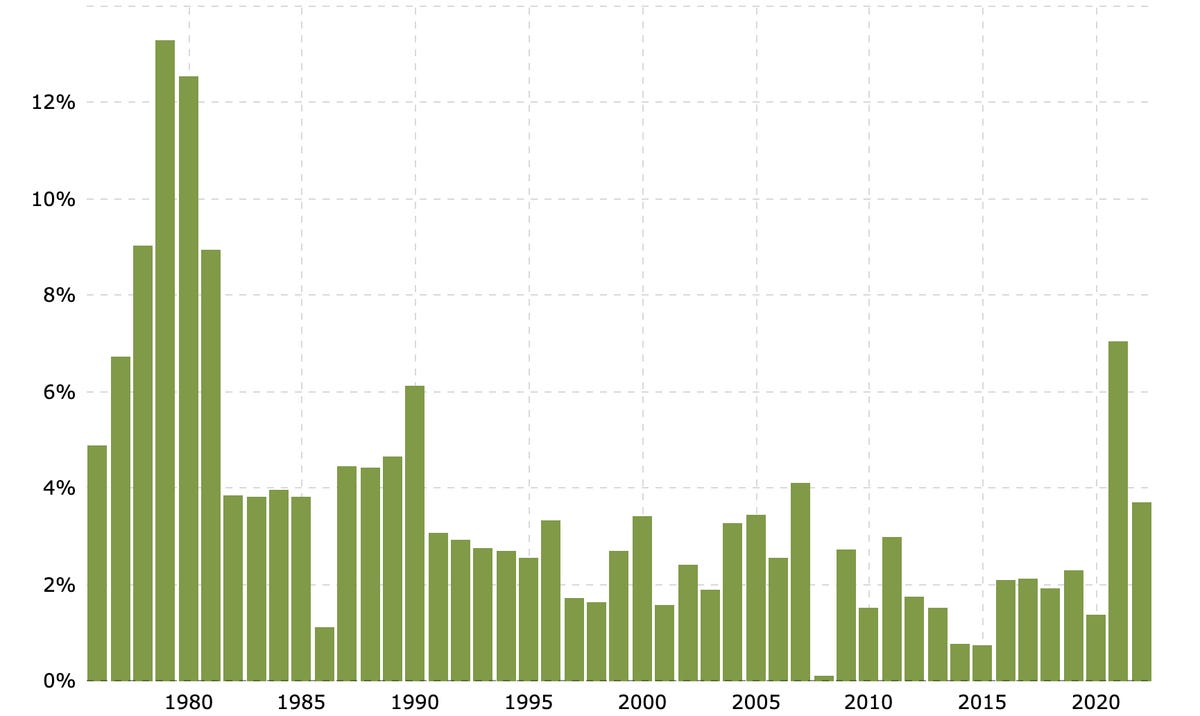
Mortgage rates are leveling off after climbing steadily since the beginning of the year. Although rates reached historic lows during the COVID-19 pandemic, they quickly reached their highest levels since 2008 earlier this year. Interest rates have been increasing in response to surging inflation, which is at its highest point in four decades, as well as the Federal Reserve raising rates multiple times for the first time since 2018. The Fed raised interest rates by 0.75 percentage points for the second time in July, one of the largest rate hikes since 1994.
Higher interest rates have significant implications for home buyers, especially as home prices remain sky-high. Higher mortgage rates, even by a few tenths of a percentage point, can add tens of thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. Higher rates shouldn't discourage you from buying a home, however. Even though rates have escalated, it's still a great time to lock in a mortgage rate, since rates are still historically low overall. Although rates crept back up and are now hovering in the mid-to-upper 5% range, generally speaking, in a rising rate environment, the sooner you act, the better, because it can help you secure a lower rate.
"Mortgage rates have bounded more than 2 percentage points higher since the end of last year, one the largest and fastest increases ever seen," said Greg McBride, chief financial analyst at CNET's sister site Bankrate.
Here's everything you need to know about mortgage rates and how they work.
What is a mortgage rate?
Your mortgage rate is the percentage of interest a lender charges for providing the loan you need to purchase a home. The interest helps cover the costs associated with lending money -- and there are multiple factors that determine the rate you're offered. Some are specific to you and your financial situation and others are influenced by macro market conditions, such as the overall level of demand for loans in your area or nationwide.
What factors determine my mortgage rate?
The factors that most often determine a mortgage rate are your credit score, the property's location, the size of the down payment, the terms of the loan and the type of loan.
"A lot of mortgages are [paid back in 360 payments] over 30 years. Shorter-term loans, like 10, 15 or 20 years have lower interest rates," says Clint Lotz, president and founder of the predictive credit tech company TrackStar. "A larger down payment means a lower interest rate; if a homebuyer can make the 20% down payment, that's great, but if not, lenders will usually require the buyer to purchase PMI: private mortgage insurance."
In addition to the loan term, the loan type will impact your interest rate. Some loans have a fixed interest rate for the entire life of the loan, while others have an adjustable rate -- which could result in significantly higher payments down the road.
Current mortgage and refinance rates
We use information collected by Bankrate, which is owned by the same parent company as CNET, to track daily mortgage rate trends. The above table summarizes the average rates offered by lenders across the country.
What credit score do you need to get a mortgage?
Most conventional loans require a credit score of 620 or higher, but Federal Housing Administration and other loan types may accommodate lenders with scores as low as 500, depending on your down payment. If you have a high credit score, you may be offered a lower interest rate and more modest down payment. Improving your credit score before applying for a mortgage can save you money even if you already qualify for a loan.
"Credit is the biggest factor in interest rates on both mortgages and all other lending products, so making sure credit balances are below 30% is key to maximizing a credit score," says Lotz. "If a person finds errors on their credit report, they should dispute them to ensure the most accurate history."
What is annual percentage rate, and what does it mean for mortgages?
Your annual percentage rate is a key factor in choosing a mortgage. The Federal Open Market Committee lowered the US prime rate in 2020, which paved the way for today's relatively low rates: The interest rate offered to you by a lender is based on the prime rate plus whatever premium the institution decides to charge you, based on your financial situation.
How does the APR impact principal and interest?
Most mortgage loans are based on an amortization schedule: You'll pay the same amount each month for the life of the loan even though the generated interest will be highest at the beginning of the loan and will taper as the principal decreases. (Your amortization schedule will show how much of your monthly payment goes to interest and how much pays down the principal of the loan.) Ultimately, most borrowers appreciate the convenience of a fixed, predictable monthly payment.
What else can impact my rate?
Getting a good mortgage rate has to do with building credit but also managing it well, including saving for a down payment and keeping additional savings on hand to cover unexpected expenses.
In most cases, you don't want to stretch so far with your down payment that you are left without cash reserves when you move into your home, and keeping some liquid savings may help your lender's confidence in your ability to pay back the loan, potentially lowering your rate.
"Banks are very keen on making sure that borrowers have sufficient savings in reserve post-closing. A good rule of thumb is six months of mortgage/tax and insurance for loans under $750,000 and 12 months for jumbo loans," says Melissa Cohn, an executive mortgage banker at Connecticut-based William Raveis Mortgage.
Keep in mind that credit scoring services like FICO adjust your credit based on mortgage inquiries; Lotz has a good piece of advice for those who are shopping around for the best rate at different lenders.
"The FICO company allows multiple mortgage inquiries within a 10-day period to be counted as one," says Lotz. "This allows a borrower to compare offers and rates from different lenders, but borrowers need to make sure they are within that one-day window, otherwise their scores will start to go down from excessive inquiries."
Shopping mortgage rates
Mortgage lenders often publish online their rates for different mortgage types, which can help you research and narrow down which lenders you apply to for preapproval. Shopping around is an important part of the process. And it's often a mistake to rush the process.
"The best rate [should be considered] -- but as important, the best service and with a reliable lender who can close the promised rate," says Cohn. "It's one thing -- especially right now -- to get quoted a rate. It's a very different matter of closing it in a timely fashion."
Source
Tags:
- Compare Current Mortgage Rates
- Current Rates Mortgage Rates
- Current Mortgage Rates Now
- Current Mortgage Rates Compare
- Compare Current Mortgage Rates Canada
- Compare Current Mortgage Interest Rates
- Compare Current Mortgage Refinance Rates
- Current Mortgage Rates Alberta
- Current Mortgage Rates Rbc
- Current Mortgage Interest Rates Ontario
- Current Mortgage Interest Rates Canada
- Current Mortgage Rates Canada 2022