Inflation, Interest Rates and Jobs: How Today's Economy Compares to Recessions of the Past
This story is part of Recession Help Desk, CNET's coverage of how to make smart money moves in an uncertain economy.
What's happening
There's still debate about whether the US economy is officially headed into a recession, but the economic downturn is causing widespread stress.
Why it matters
Periods of financial volatility and market decline can drive people to panic and make costly mistakes with their money.
What's next
Examining what's happening now -- and comparing it with the past -- can help investors and consumers decide what to do next.
Facing the aftershocks of a rough economy in the first half of 2022, with sky-high inflation, rising mortgage rates, soaring gas prices and a bear market for stocks, leading indicators of a recession have moderated slightly in the past month. That could mean the economic downturn won't be as long or brutal as expected.
Still, the majority of Americans are feeling the sting of rising prices and anxiety over jobs. The country has experienced two consecutive quarters of economic slowdown -- the barometer for measuring a recession -- even though the National Bureau of Economic Research hasn't made the "official" recession call.
At a time like this, we should consider what happens in a recession, look at the data to determine whether we're in one and try to maintain some historical perspective. It's also worth pointing out that down periods are temporary and that, over time, both the stock market and the US economy bounce back.
I don't mean to minimize the gravity and hardship of the times. But it can be useful to review how the economy has behaved in the past to avoid irrational or impulsive money moves. For this, we can largely blame recency bias, our inclination to view our latest experiences as the most valid. It's what led many to flee the stock market in 2008 when the S&P 500 crashed, thereby locking in losses and missing out on the subsequent bull market.
"It's our human tendency to project the immediate past into the future indefinitely," said Daniel Crosby, chief behavioral officer at Orion Advisor Solutions and author of The Laws of Wealth. "It's a time-saving shortcut that works most of the time in most contexts but can be woefully misapplied in markets that tend to be cyclical," Crosby told me via email.
Before you make a knee-jerk reaction to your portfolio, give up on a home purchase or lose it over job insecurity, consider these chart-based analyses from the last three decades. We hope this data-driven overview will offer a broader context and some impetus for making the most of your money today.
What do we know about inflation?
Historical inflation rate by year
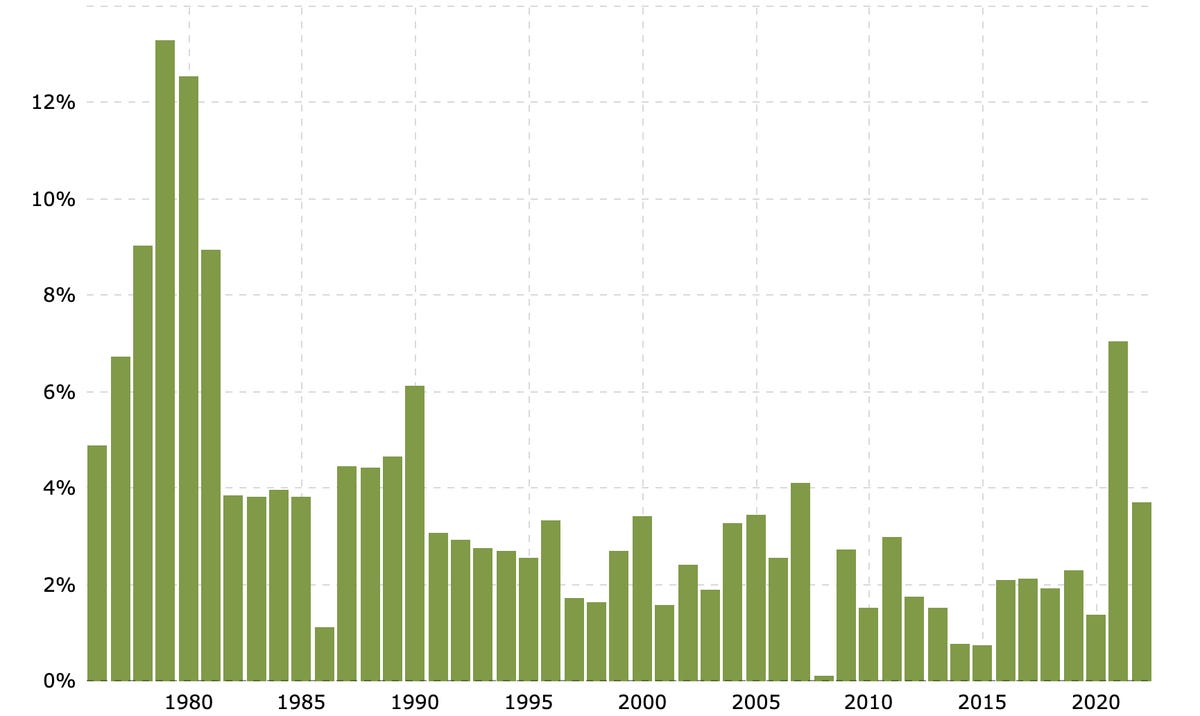
Current conditions: The US is experiencing the highest rate of inflation in decades, driven by global supply chain disruptions, the injection of federal stimulus dollars and a surge in consumer spending. In real dollars, the 8.5% rise in consumer prices over the past year is adding about $400 more per month to household budgets.
The context: Policymakers consider 2% per year to be a "normal" inflation target. The country's still experiencing over four times that figure. The 9.1% annual rate in July was the largest jump in inflation since 1980 when the inflation rate hit 13.5% following the prior decade's oil crisis and high government spending on defense, social services, health care, education and pensions. Back then, the Federal Reserve increased rates to stabilize prices and, by the mid-1980s, inflation fell to below 5%.
The upside: As overall inflation rates rise, the silver lining might be increased rates of return on personal savings. Bank accounts are starting to offer more attractive yields, while I bonds -- federally backed accounts that more or less track inflation -- are attracting savers, too.
What's happening with mortgage rates?
30-year fixed-rate mortgage averages in the US
Current conditions: As the Federal Reserve continues its rate-hike campaign to cool spending and try to tame inflation, the rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage has grown significantly. In June, the average rate jumped annually by nearly 3 percentage points to almost 6%. In real dollars, that means that after a 20% down payment on a new home (let's use the average sale price of $429,000), a buyer would roughly need an extra $7,300 a year to afford the mortgage. Since then, rates have cooled a bit, even dipping back down below 5%. What happens next with rates depends on where inflation goes from here.
The context: Three years ago, homebuyers faced similar borrowing costs and, at the time, rates were characterized as "historically low." And if we think borrowing money is expensive today, let's not forget the early 1980s when the Federal Reserve jacked up rates to never-before-seen levels due to hyperinflation. The average rate on a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage in 1981 topped 16%.
The upside: For homebuyers, a potential benefit to rising rates is downward pressure on home prices, which could cause the housing market to cool slightly. As the cost to borrow continues to increase with mortgages becoming more expensive, homes could experience fewer offers and prices would slow in pace. In fact, nearly one in five sellers dropped their asking price during late April through late May, according to Redfin.
On the flip side, less homebuyers mean more renters. Rent prices have skyrocketed, and housing activists are asking the White House to take action on what they call a "national emergency."
What about the stock market?
Dow Jones Industrial Average stock market index for the past 30 years

Current conditions: Year-to-date, the Dow Jones Industrial Average -- a composite of 30 of the most well-known US stocks such as Apple, Microsoft and Coca-Cola -- is about 8.5% below where it started in January. Relative to the broader market, technology stocks are down much more. The Nasdaq is off almost 19% since the start of the year.
The benchmark S&P 500 stock index hit lows in June that marked a more than 20% drop from January, which brought us officially into a bear market. Since then, it's bounced back up a little, but some experts warn that a current bear market rally is at odds with expected earnings and we could see even lower stock prices in the near future.
The context: Stock price losses in 2022 are not nearly as swift and steep as what we saw in March 2020, when panic over the pandemic drove the DJIA down by 26% in roughly four trading days. The market reversed course the following month and began a bull run lasting more than two years, as the lockdown drove massive consumption of products and services tied to software, health care, food and natural gas.
Prior to that, in 2008 and 2009, a deep and pervasive crisis in housing and financial services sank the Dow by nearly 55% from its 2007 high. But by fall 2009, it was off to one of its longest winning streaks in financial history.
The upside: Given the cyclical nature of the stock market, now is not the time to jump ship.* "Times that are down, you at least want to hold and/or think about buying," said Adam Seessel, author of Where the Money Is. "Over the last 100 years, American stocks have been the surest way to grow wealthy slowly over time," he told me during a recent So Money podcast.
*One caveat: If you're closer to or living in retirement and your portfolio has taken a sizable hit, it may be worth talking to a professional and reviewing your selection of funds to ensure that you're not taking on too much risk. Target-date funds, a popular investment vehicle in many retirement accounts that auto-adjust for risk as you age, may be too risky for pre- or early retirees.
What does unemployment tell us?
US unemployment rates
Current conditions: The July jobs report shows the unemployment rate holding steady, slightly dropping to 3.5%. The Great Resignation of 2021, where millions of workers quit their jobs over burnout, as well as unsatisfactory wages and benefits, left employers scrambling to fill positions. However, that could be changing as economic challenges deepen: More job losses are likely on the horizon, and an increasing number of workers are concerned with job security.
The context: The rebound in theunemployment rate is an economic hallmark of the past two years. But the ongoing interest rate hike may weigh on corporate profits, leading to more layoffs and hiring freezes. For context, during the Great Recession, in a two-year span from late 2007 to 2009, the unemployment rate rose sharply from about 5% to 10%.
Today, the tech sector is one to watch. After benefiting from rapid growth led by consumer demand in the pandemic, companies like Google and Facebook may be in for a "correction." Layoffs.fyi, a website that tracks downsizing at tech startups, logged close to 37,000 layoffs in Q2, more than triple from the same period last year.
The upside: If you're worried about losing your job because your employer may be more vulnerable in a recession, document your wins so that when review season arrives, you're ready to walk your manager through your top-performing moments. Offer strategies for how to weather a potential slowdown. All the while, review your reserves to see how far you can stretch savings in case you're out of work. Keep in mind that in the previous recession, it took an average of eight to nine months for unemployed Americans to secure new jobs.
§
What's happening
Home prices overall are up by 37% since March 2020.
Why it matters
Surging home prices and higher interest rates make monthly mortgage payments less affordable.
What's next
Rising mortgage rates will make borrowing money more expensive, which will lessen competition to buy homes and eventually flatten prices.
Home prices continued to skyrocket in March as buyers tried to stay ahead of rising mortgage rates.
Prices increased by 20.6% this March compared to last year, according to the S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller Indices, the leading measures of US home prices. This was the highest year-over-year increase in March for home prices in more than 35 years of data. Seven in 10 homes sold for more than their asking price, according to CoreLogic.
Out of the 20 cities tracked by the 20-city composite index, Tampa, Phoenix and Miami saw the highest year-over-year gains in March. Tampa saw the greatest increase, with an almost 35% increase in home prices year-over-year. All 20 cities experienced double-digit price growth for the year ending in March.
The strongest price growth was seen in the south and southeast, with both regions posting almost 30% gains in March. Seventeen of the 20 metro areas also saw acceleration in their annual gains since February.
"Those of us who have been anticipating a deceleration in the growth rate of US home prices will have to wait at least a month longer," said Craig Lazzara, managing director at S&P DJI, in the release. "The strength of the Composite indices suggests very broad strength in the housing market, which we continue to observe."
Since the start of the pandemic in March 2020, home prices overall are up by 37%. The current surge in home prices is a result of tight competition between buyers in a low-inventory market as they attempt to lock in lower mortgage rates before rates jump even higher throughout the year, as experts predict they will.
If you're considering buying a new home -- or are actively in the market -- the news isn't all bad. Interest rates are at their highest point in more than 40 years, and one potential benefit of that may, eventually, be downward pressure on home prices. As it becomes increasingly expensive to borrow money, fewer people will seek to do so, and homes for sale may receive fewer offers leading to, eventually, lower prices. In fact, nearly one in five sellers lowered their asking price during a four-week period in May and April, according to Redfin.
"Mortgages are becoming more expensive as the Federal Reserve has begun to ratchet up interest rates, suggesting that the macroeconomic environment may not support extraordinary home price growth for much longer," said Lazzara. "Although one can safely predict that price gains will begin to decelerate, the timing of the deceleration is a more difficult call."
Source
Tags:
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How Today S Unions Help Working People
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How Today The Rosary
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How Today Stencile
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How Today Contact
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How Today Weather
- Inflation Interest Rates And Jobs How To Find
- Inflation Interest Rates And Recession
- Inflation Interest Rates And Recession
- Relationship Between Inflation Interest Rates
- Inflation Interest Rates
- Inflation Interest Rates And Recession
- Inflation Interest Rate Calculator