Twitter could cut back on hate speech with suspension warnings, study says
Since Twitter launched in 2006, it's become a giant networking event, bar hangout, meme-generator and casual conversation hub stuffed into one. But for every 280-word-long timely news update and witty remark, you'll find a violent, hateful post.
Among the crew of experts strategizing to disarm the dark side of Twitter, a team from New York University ran an experiment to test whether warning accounts that hate speech will result in suspension is a functional technique. Turns out, it could be pretty effective.
After studying over 4,300 Twitter users and 600,000 tweets, the scientists found warning accounts of such consequences "can significantly reduce their hateful language for one week." That dip was even more apparent when warnings were phrased politely.
Hopefully the team's paper, published Monday in the journal Perspectives on Politics, will help address the racist, vicious and abusive content that pollutes social media.
"Debates over the effectiveness of social media account suspensions and bans on abusive users abound, but we know little about the impact of either warning a user of suspending an account or of outright suspensions in order to reduce hate speech," Mustafa Mikdat Yildirim, an NYU doctoral candidate and the lead author of the paper, said in a statement.
"Even though the impact of warnings is temporary, the research nonetheless provides a potential path forward for platforms seeking to reduce the use of hateful language by users."
These warnings, Mikdat Yildirim observed, don't even have to come from Twitter itself. The ratio of tweets containing hateful speech per user lowered by between 10% and 20% even when the warning originated from a standard Twitter account with just 100 followers -- an "account" made by the team for experimental purposes.
"We suspect, as well, that these are conservative estimates, in the sense that increasing the number of followers that our account had could lead to even higher effects...to say nothing of what an official warning from Twitter would do," they write in the paper.
At this point you might be wondering: Why bother "warning" hate speech endorsers when we can just rid Twitter of them? Intuitively, an immediate suspension should achieve the same, if not stronger, effect.
Why not just ban hate speech ASAP?
While online hate speech has existed for decades, it's ramped up in recent years, particularly toward minorities. Physical violence as a result of such negativity has seen a spike as well. That includes tragedies like mass shootings and lynchings.
But there's evidence to show unannounced account removal may not be the way to combat the matter.
As an example, the paper points out former President Donald Trump's notorious and erroneous tweets following the 2020 United States presidential election. They consisted of election misinformation like calling the results fraudulent and praise for rioters who stormed the Capitol on January 6, 2021. His account was promptly suspended.
Twitter said the suspension was "due to the risk of further incitement of violence," but the problem was Trump later attempted to access other ways of posting online, such as tweeting through the official @Potus account. "Even when bans reduce unwanted deviant behavior within one platform, they might fail in reducing the overall deviant behavior within the online sphere," the paper says.
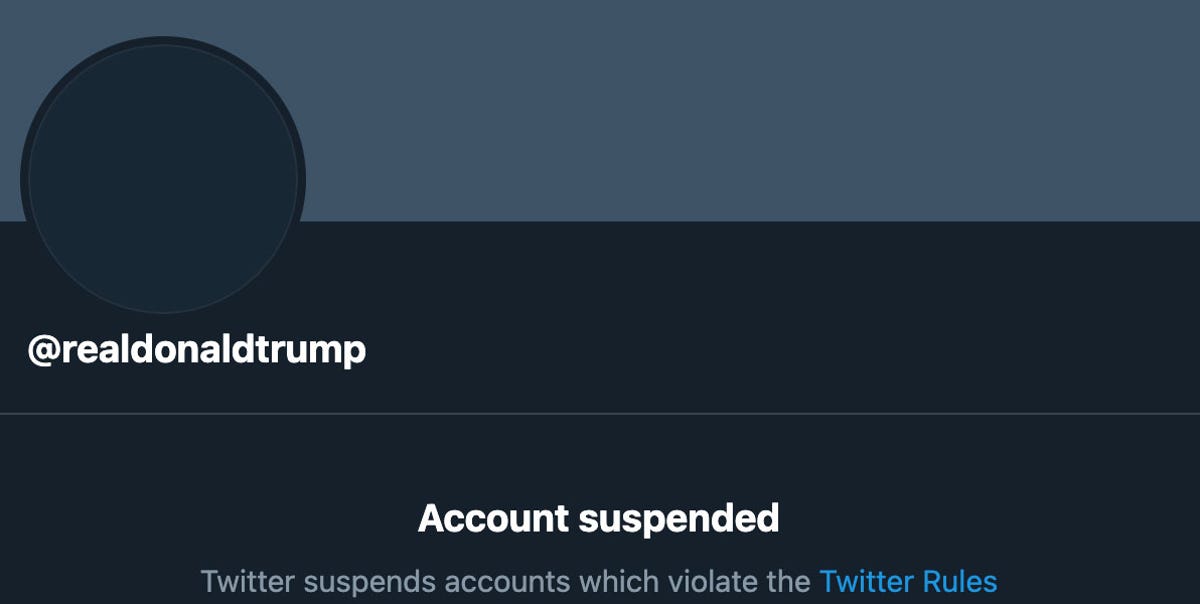
Twitter suspended President Donald Trump's Twitter account on Jan. 8, 2021.
Screenshot by Stephen Shankland/CNETIn contrast to quick bans or suspensions, Mikdat Yildirim and fellow researchers say warnings of account suspension could curb the issue long term because users will try to protect their account instead of moving somewhere else as a last resort.
Experimental evidence for warning signals
There were a few steps to the team's experiment. First, they created six Twitter accounts with names like @basic_person_12, @hate_suspension and @warner_on_hate.
Then, they downloaded 600,000 tweets on July 21, 2020 that were posted the week prior to identify accounts likely to be suspended during the course of the study. This period saw an uptick in hate speech against Asian and Black communities, the researchers say, due to COVID-19 backlash and the Black Lives Matter movement.
Sifting through those tweets, the team picked out any that used hate language as per a dictionary outlined by a researcher in 2017 and isolated those created after January 1, 2020. They reasoned that newer accounts are more likely to be suspended -- over 50 of those accounts did, in fact, get suspended.
Anticipating those suspensions, the researchers gathered 27 of those accounts' follower lists beforehand. After a bit more filtering, the researchers ended up with 4,327 Twitterers to study. "We limited our participant population to people who had previously used hateful language on Twitter and followed someone who actually had just been suspended," they clarify in the paper.
Next, the team sent warnings of different politeness levels -- the politest of which they believe created an air of "legitimacy" -- from each account to the candidates divided into six groups. One control group didn't receive a message.
Legitimacy, they believe, was important because "to effectively convey a warning message to its target, the message needs to make the target aware of the consequences of their behavior and also make them believe that these consequences will be administered," they write.
Ultimately, the method led to a reduction in the ratio of hateful posts by 10% for blunt warnings, such as "If you continue to use hate speech, you might lose your posts, friends and followers, and not get your account back" and by 15% to 20% with more respectful warnings, which included sentiments like "I understand that you have every right to express yourself but please keep in mind that using hate speech can get you suspended."
But it's not that simple
Even so, the research team notes that "we stop short, however, of unambiguously recommending that Twitter simply implement the system we tested without further study because of two important caveats."
Foremost, they say a message from a large corporation like Twitter could create backlash in a way the study's smaller accounts did not. Secondly, Twitter wouldn't have the benefit of ambiguity in suspension messages. They can't really say "you might" lose your account. Thus, they'd need a blanket rule.
And with any blanket rule, there could be wrongfully accused users.
"It would be important to weigh the incremental harm that such a warning program could bring to an incorrectly suspended user," the team writes.
Although the main impact of the team's warnings dematerialized about a month later and there are a couple of avenues yet to be explored, they still urge this technique could be a tenable option to mitigate violent, racist and abusive speech that continues to imperil the Twitter community.
Source