Intel's Alder Lake chip could speed PCs by 30% while saving battery power
Intel's new Alder Lake processor could boost the performance of personal computers by as much as 30% while delivering longer battery life, a breakthrough the chipmaker credits to a hybrid design that marries modules for top speed with others for efficient operation. It's an approach that's been used for years in smartphones.
At its Architecture Day event on Thursday, Intel said Alder Lake chips will come in three broad classes to power mainstream laptops, ultralight laptops and beefier desktop PCs. The three classes will be modeled on smartphone chips that combine high-performance computing cores for demanding jobs with smaller efficient cores that don't sap as much energy.
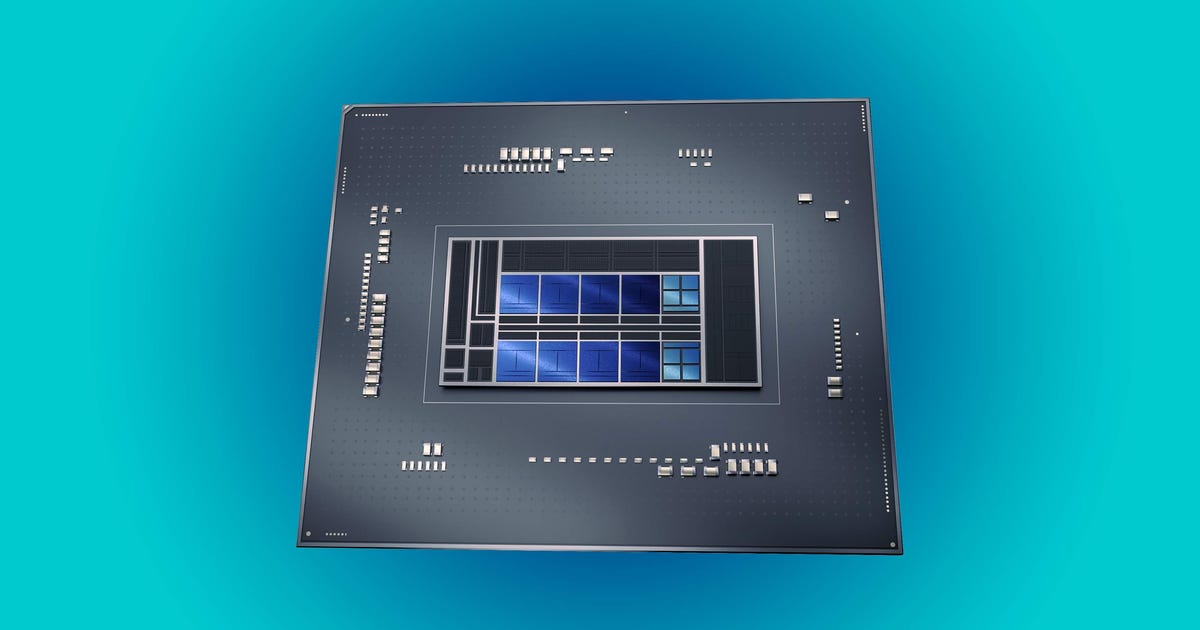
The number of performance and efficiency cores differ for each variety, but the fastest model will have eight of each. Intel's diagrams showed mobile Alder Lake chips combining six performance cores with eight efficiency cores and ultramobile chips combining two performance cores with eight efficiency cores. The Alder Lake family of chips will be available in PCs this fall.
The power and efficiency boost over today's 11th-gen Core models code-named Tiger Lake are a crucial selling point now that we have grown to expect laptops that can run for an entire day unplugged. Intel already competes with Apple and its M1 Mac processor that delivers improved power and battery life.
"We want [to] combine the best of both best of both in one system," Raja Koduri, who runs Intel's Accelerated Computing Systems & Graphics group, said in an advance briefing. Alder Lake's hybrid approach will help chart Intel's course for the next decade, Intel said.
Alder Lake's hybrid architecture is a variation of the Big.Little design that chip designer Arm rolled out a decade ago and now dominates smartphones. Apple employs the same approach with the M1 chip, which began powering Macs in 2020 and likely will be upgraded for more powerful Macs expected this year.
Alder Lake marks an important moment of unification and simplification for Intel's chip product line. Intel has been juggling a hodgepodge of new and old designs as it struggled with delays to its manufacturing process. The company fell behind its competitors as it wrangled with the problems, with AMD chip designs gaining market share, Apple ejecting Intel chips from its Macs and Asian giants Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) and Samsung leapfrogging Intel in chip manufacturing.
Now all Intel's PC chips will be built with a manufacturing process called Intel 7. The same goes for Alder Lake's big sibling, Sapphire Rapids, a server chip due to arrive in the first half of 2022. Reducing the complexity should lower Intel's costs.
The chips were designed before Pat Gelsinger rejoined Intel earlier this year as chief executive. But they're an important part of his attempt to reclaim Intel's lost chipmaking leadership. He's also overseeing Intel's launch of a foundry business that builds chips for other companies, including rival Qualcomm, and hiring rival TSMC to build parts of its own chips.
"Intel is getting back to the Intel of old," said Tirias Research analyst Kevin Krewell, with the company rebuilding its past technical and operational acumen.
How much faster and more efficient will Alder Lake be?
Intel has been cagey with details but released some measurements of Alder Lake.
An average of speed tests shows Alder Lake's performance cores, known by the code name Golden Cove, demonstrates a 19% boost over today's Tiger Lake chips while running at the same clock speed, said Adi Yoaz, director of the Intel Core architecture. "This is our largest architectural shift in over a decade," he said.

Intel Alder Lake processors likely will all come with eight high-efficiency cores, shown in blue, for lower priority tasks and battery-saving operations. The number of high-performance cores, shown in purple, will range from eight on beefy desktop processors to two on ultramobile devices.
IntelThe new manufacturing process should add another 10% to 15% through hardware refinements that improve attributes like clock speed. Together, that could mean a 30% or more boost in top speeds, a big step up from past annual improvements typically less than 10%.
For preserving battery life while running a set of lower priority tasks, the Gracemont efficient core's design improves Intel's over earlier Skylake design, which is still widely used even though it's six years old. While juggling four tasks at once, efficiency cores require a fifth the power of Skylake cores, said Intel chip architect Stephen Robinson.
Using a technology called Thread Director, Alder Lake will determine whether computing jobs should be assigned to performance or efficiency cores or be shuffled around as new tasks arrive. Thread Director requires support built into Microsoft's upcoming Windows 11, but the current Windows 10 will be able to tap into some of its multicore features, said Rajshree Chabukswar, an engineer on the Alder Lake team.
Intel buying chips from rival TSMC
At Architecture Day, Intel revealed that TSMC, the foundry that builds Apple iPhone and Mac chips, will build Alchemist, the first member of Intel's new Arc family of standalone graphics chips. The chip is due early next year.
TSMC will also build Intel-designed graphics chips core to Ponte Vecchio, a massive processor package with high-speed links between many different chip elements. Ponte Vecchio will be the main brains of the Energy Department's $500 million Aurora supercomputer at Argonne National Laboratory. (Slow development of the processor has delayed the arrival of that machine.)
Expect Ponte Vecchio's array of packaging technologies -- an Intel manufacturing advantage -- to trickle down to mainstream products, said Real World Technologies analyst David Kanter.
"Ponte Vecchio is the Lamborghini of the chip world. Will this become the Lexus and then become the Toyota?" he asked. "The answer is yes."
Other Alder Lake chip specs
Alder Lake processors will come in varieties consuming as little as 9 watts for ultramobile devices and 125 watts for the beefy desktops used for the most demanding tasks like gaming and video editing.
The new chip is faster thanks to a variety of improvements in how it fetches instructions to execute, caches data instructions in high-speed memory, predicts the instructions it expects to run and recovers from mistakes in those predictions.
And it gets new instructions to execute artificial intelligence tasks with a technology called Advanced Matrix Extensions. AI is an immensely important new type of computer work, and many chip designers -- including Apple, Google, Qualcomm, Samsung, Arm and many startups -- are building dedicated AI acceleration electronics into chips.
Also built into Alder Lake are controllers to handle faster new memory standards, DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5) memory and, for mobile devices, LPDDR5 (Low Power Double Data Rate 5). Faster memory helps keep the processor fed with data so it doesn't have to spend as much time idling.
For connecting to the other devices like network controllers and graphics cards, Alder Lake chips debut support for the new fifth-generation PCI Express. That can double data transfer speed compared to PCIe 4.
Source





