9 Great Reads From CNET This Week: iOS 16, Metaverse, Ms. Marvel and More
This week brought us Apple's annual Worldwide Developers Conference, when the maker of Macs and iPhones shares details of coming changes to the software that runs those and other devices. WWDC is on the geeky side, but it's also pretty clear what's in store for everyone who uses Apple products.
We found out, for instance, about iOS 16, coming to iPhones later this year with features like an updated lock screen heavy on customization; Apple Pay Later, which splits the cost of a purchase across four payments; and Safety Check, designed to help people at risk of abuse. We got a peek at MacOS Ventura, along with a redesigned MacBook Air and a 13-inch MacBook Pro, both of which will pack the new M2 chip. And we learned about WatchOS 9 and iPadOS 16, too.
Our stories about WWDC came to you among the many in-depth features and thought-provoking commentaries that also appeared on CNET this week. So here you go. These are the stories you don't want to miss.
Commentary: Apple's changes to the iPhone lock screen are a bigger deal than you think.

Commentary: Moderating social media is hard. Moderating the metaverse will be harder.

As tech's reach grows, companies are taking on a new, very personal, set of issues.

Here's why people freeze in place and have waking nightmares.

The new MCU series about a Pakistani Muslim-American superhero shows just how far Hollywood has come.

I don't recommend it.

Initial analysis of the samples from asteroid Ryugu show the rock could change our understanding of the early solar system.

Commentary: WatchOS 9's new running features could pair nicely with the rumored Apple Watch Explorer Edition.

Google, Apple, and Microsoft expect passkeys can completely replace passwords. Apple support arrives in iOS 16 and MacOS Ventura.

§
This story is part of WWDC 2022, CNET's complete coverage from and about Apple's annual developers conference.
What's happening
Apple's WatchOS 9 update will bring new athletic performance metrics to the Apple Watch, among other key improvements to health and fitness tracking.
Why it matters
The update could be setting the stage for the rumored rugged Apple Watch expected to debut this year.
What's next
Apple will launch WatchOS 9 in the fall, possibly alongside three new Apple Watch models.
If WatchOS 9 serves as any indication, the Apple Watch's future is all about health and fitness. That message was front and center in June when Apple unveiled the new software, which is now available in beta ahead of its fall launch.
The update will bring more sports-performance tracking metrics (especially for runners), deeper sleep monitoring and tools for logging medication. It's impossible to know what to expect until Apple announces its next smartwatch (or smartwatches). But WatchOS 9's focus on athletic training seemingly sets the stage for the rumored Apple Watch Explorer Edition, which we might see later this year.
Read more: This Stylish, Luxury Hybrid Watch (Almost) Made Me Ditch My Apple Watch
It also suggests Apple wants its smartwatch to appeal to pro athletes, casual exercise enthusiasts and those who need to monitor cardiac health all at the same time. The next crop of Apple Watches rumored for the fall will likely come with new hardware to better support that vision -- hopefully with better battery life, too.
WatchOS 9's workout features would be a great for an Explorer Edition Apple Watch

The Apple Watch Series 7
Lexy Savvides/CNETApple sprinkled a bunch of new workout tools and metrics throughout WatchOS 9. These include new running data points like stride length and ground contact time, the ability to track heart rate zones, interval training, a multisport workout type for triathlons and kickboard detection for swimmers. The announcement also comes after Apple made improvements to the Apple Watch's cycling detection last year.
Only Apple knows what's in store for the future. But it feels like no coincidence that this update is coming as Apple is expected to launch a rugged Apple Watch designed for extreme sports this fall. Bloomberg reports an Apple Watch with extra impact resistance similar to Casio's G-Shock watches could be in the works. The watch is sometimes referred to as the Explorer Edition internally and may have a rubberized casing for additional durability, the report said. The device would reportedly be marketed as an alternative option for athletes and hikers alongside the standard Series 8 and next-generation Apple Watch SE.
Read more: iOS 16's Lock Screen Upgrades Make the iPhone More Like a Smartwatch
The Apple Watch already has plenty to offer fitness buffs, with many workout choices, activity goals and reminders, heart rate notifications and metrics like VO2 max and elevation. But until WatchOS 9 arrives, the Apple Watch will lack running-specific features that athletes might find useful. Garmin's running watches, for example, include tools like training programs for specific types of races, pace guidance and running metrics like cadence and stride length, among other features that vary by the model.
The Apple Watch is already the world's most popular smartwatch with 36.1% of global shipments in the first quarter of 2022, according to Counterpoint Research. With the new measurements geared toward runners coming in WatchOS 9, Apple could further solidify its grip on the market by appealing to the more niche competitive sports audience.
Even with the new features in WatchOS 9, the Apple Watch still won't offer quite as much feedback for runners as some specialized watches. But the new software certainly brings the Apple Watch closer than ever before.
What else WatchOS 9 might tell us about the Apple Watch's future
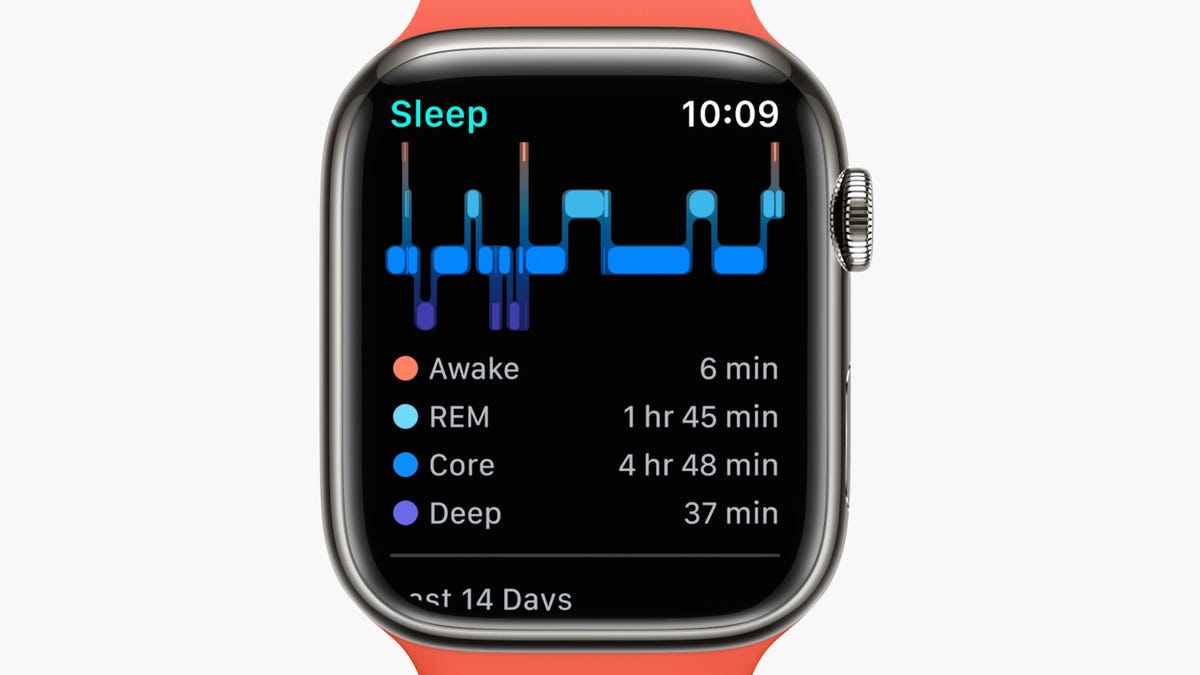
The Apple Watch's new Sleep Stages feature in WatchOS 9
Screenshot/CNETApple's emphasis on fitness was at the heart of its WatchOS 9 announcement. But some of the software's other updates might also suggest Apple's future direction. For example, the company did more on sleep tracking by introducing Sleep Stages, a feature that analyzes the amount of time spent in various phases of slumber. Apple is playing catch-up in this regard; rival fitness trackers from Fitbit, Oura and Samsung have supported this feature for years.
Apple's expansion in sleep tracking indicates it expects Apple Watches to be worn overnight more frequently. That makes me believe Apple could be planning some type of improvement to the Apple Watch's battery life, although there's no way to know for sure until the company reveals its next watch.
Apple says its smartwatch can last for 18 hours on a single charge, and anecdotally I typically get about one to two days out of it before it needs a power boost. The Apple Watch's battery life hasn't changed meaningfully in years, but Apple has worked around this by implementing faster charging speeds with the Series 6 and 7.
Apple will likely continue down this path rather than dramatically improving the watch's battery life. But there's also a chance Apple could introduce a new low-power mode with more functionality than the watch's current power reserve feature, says Bloomberg. It was supposed to launch with WatchOS 9, according to the report, although Apple didn't mention a new low-power option during Monday's event.
Considering that battery life has been one of the Apple Watch's persistent criticisms -- and not to mention Bloomberg's reliable track record -- I wouldn't be surprised to see this capability arrive in the future. And remember: Apple introduced new WatchOS 8 features for cyclists alongside the Apple Watch Series 7 during its fall product event in 2021. So there's a chance Apple could have more software features to announce later this year.
WatchOS 9 also provides another signal that Apple is expanding its efforts in general health and wellness. A new feature called AFib History will allow those diagnosed with atrial fibrillation to access more information about their condition, such as an estimate of how often their heart rhythm is showing signs of A-fib. Another highlight in WatchOS 9 is the ability to track prescriptions and receive medication reminders.
These updates indicate Apple sees its watch as a tool for tracking bodily changes over time that can be shared with physicians. And if reports from Bloomberg and The Wall Street Journal prove accurate, Apple will take that idea a step further by adding a temperature sensor to the Series 8.
Many of the Apple Watch's major turning points have historically been tied to new hardware releases. The Series 3, for example, was the first model to support cellular connectivity, making the Apple Watch feel like a stand-alone product rather than an iPhone companion. The Series 4 brought ECG monitoring and fall detection, broadening the Apple Watch's role as a health device.
WatchOS 9 isn't as big of a leap forward as those launches. But it will bring functionality that could be crucial in Apple's mission to make the Apple Watch the ultimate health and fitness device. And that's very telling of Apple's immediate and long term plans for the Apple Watch.
Source






